Understanding Bugs, Defects, Errors, Faults, and Failures in Software Testing: Essential Insights for QA Teams
Understanding the different types of issues in software testing, bugs, defects, errors, faults, and failures, is crucial for improving your development and testing processes. This edition breaks down each term and its impact on software development. For a manual tester or someone focused on automation, this guide will help you identify, categorize, and fix issues efficiently.
🔍 What You’ll Learn:
The key differences between bugs, defects, errors, faults, and failures in software testing
Practical examples of each term and their impact
The role of manual and automation testing in identifying and resolving issues
How using precise terminology improves communication and software quality assurance
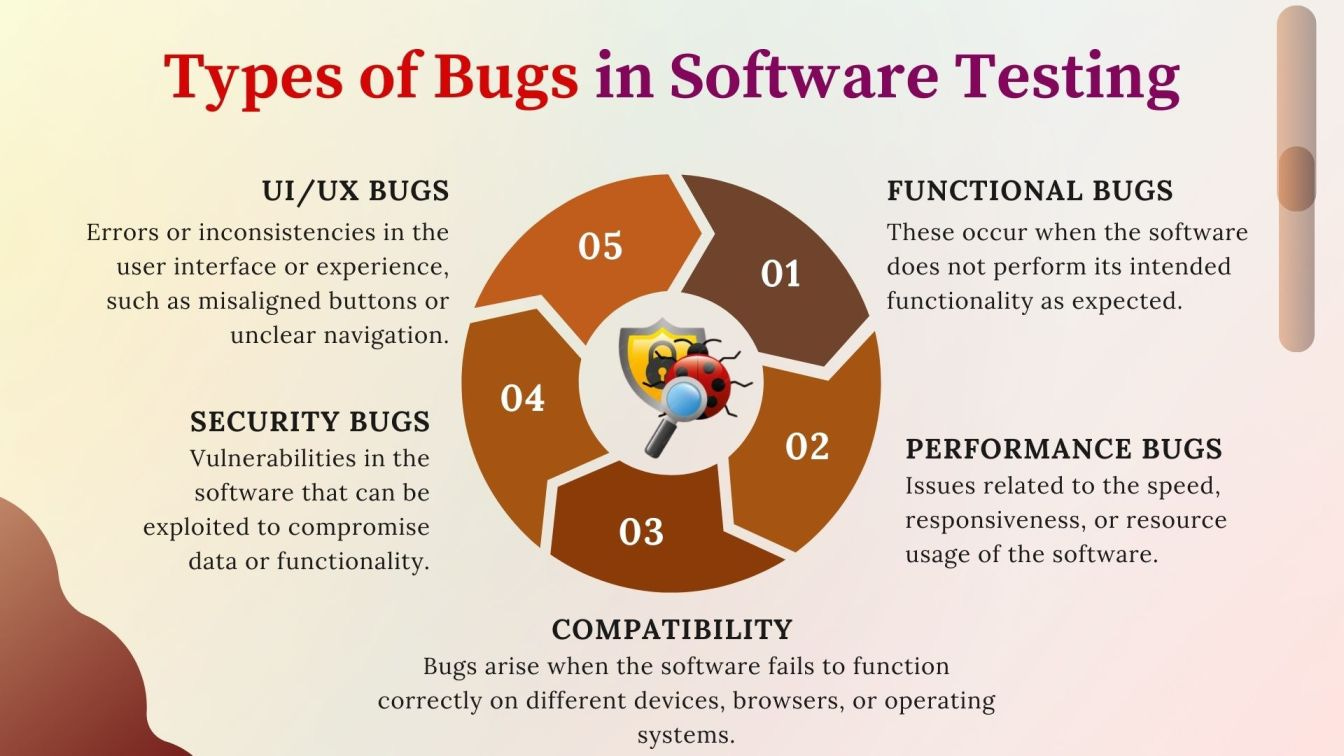
What is a Bug?
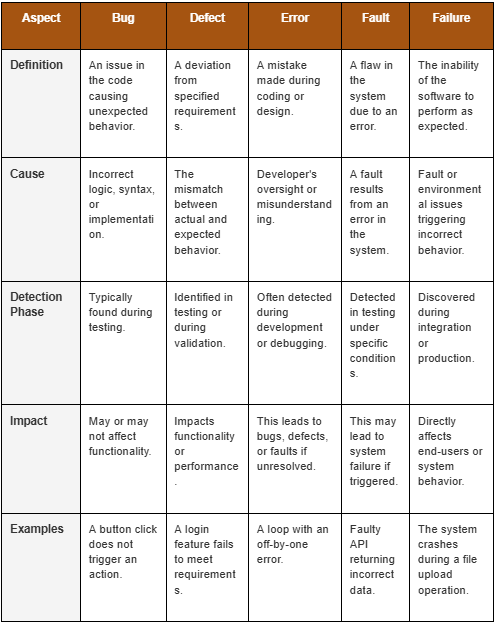
A bug is an unexpected issue in software, often caused by incorrect logic, syntax, or poor design. Bugs are typically identified during testing and can range from minor glitches to critical errors that affect the system’s functionality.
Impact of Bugs:
System Crashes
Data Loss
Security Vulnerabilities
Degraded User Experience
Increased Development Costs
Delays in Deployment
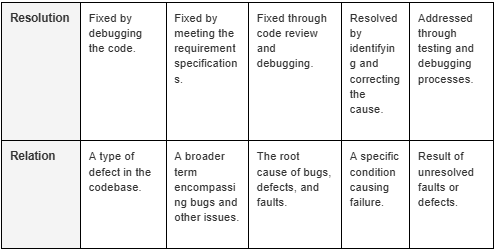
Key Takeaway: Bugs can cause major disruptions, especially if left unresolved. Early detection ensures smoother updates and higher software quality.
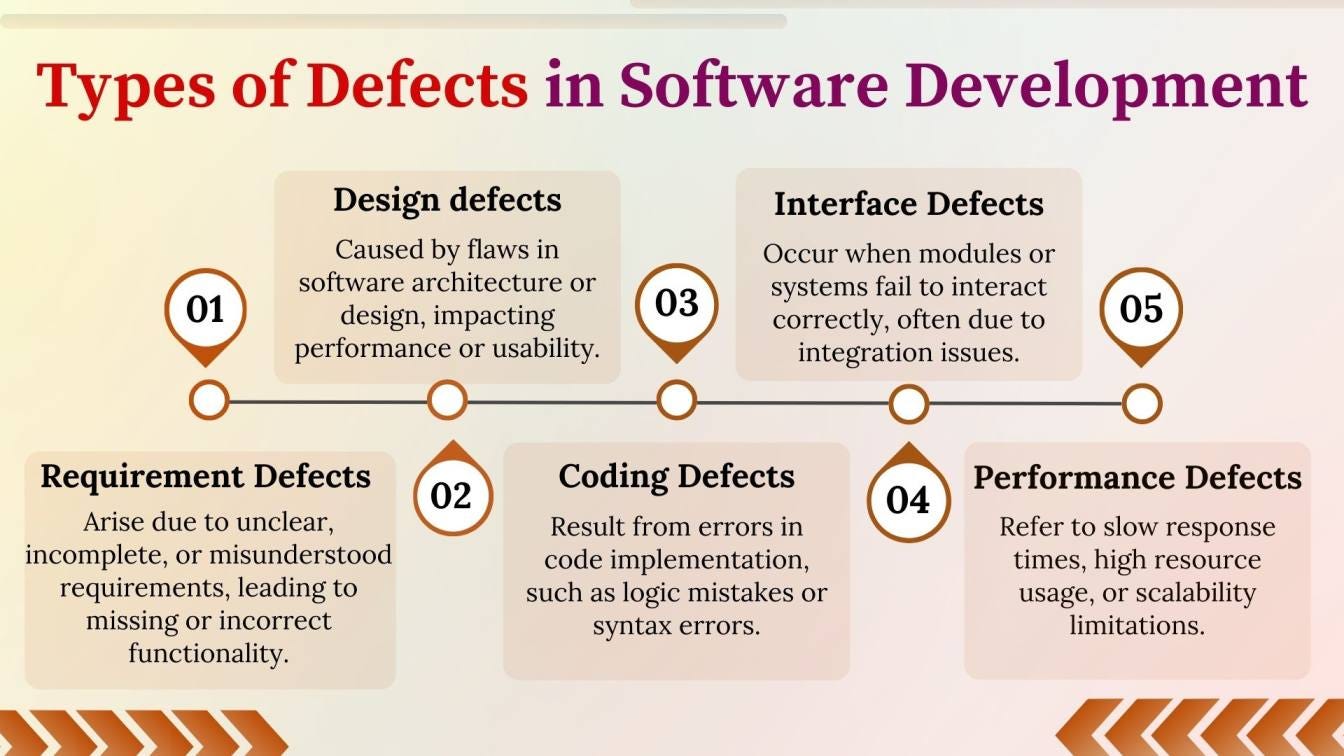
What is a Defect?
A defect refers to a flaw in the software that prevents it from performing as intended. This can occur due to incorrect implementation, incomplete requirements, or poor design during development.
Impact of Defects:
Increased Development Costs
Delayed Release Cycles
Impact on Team Productivity
Reduced Software Quality
Customer Dissatisfaction
Key Takeaway: Identifying defects early ensures better software quality and reduces the need for frequent software updates.
What is an Error?
An error occurs when a developer makes a mistake, often during coding or design. These errors lead to bugs or defects and can cause issues during testing. In API automation testing, errors might occur due to incorrect API calls or missing parameters.
Impact of Errors:
Creation of Bugs and Defects
Increased Debugging Efforts
System Instability
Incompatibility Issues
Key Takeaway: Errors, if caught early, can prevent costly delays and system instability.
What is a Fault?
A fault arises when there’s an issue in the system that leads to unexpected behavior when triggered. For example, a faulty API can return incorrect data or a database connection can fail. Faults are often detected during automation testing that simulates real-world scenarios.
Impact of Faults:
Triggering Failures in Production
Reduced System Reliability
Unexpected Behavior
Delayed Debugging in Live Environments
Key Takeaway: Faults, when ignored, can escalate into failures, impacting overall system stability.
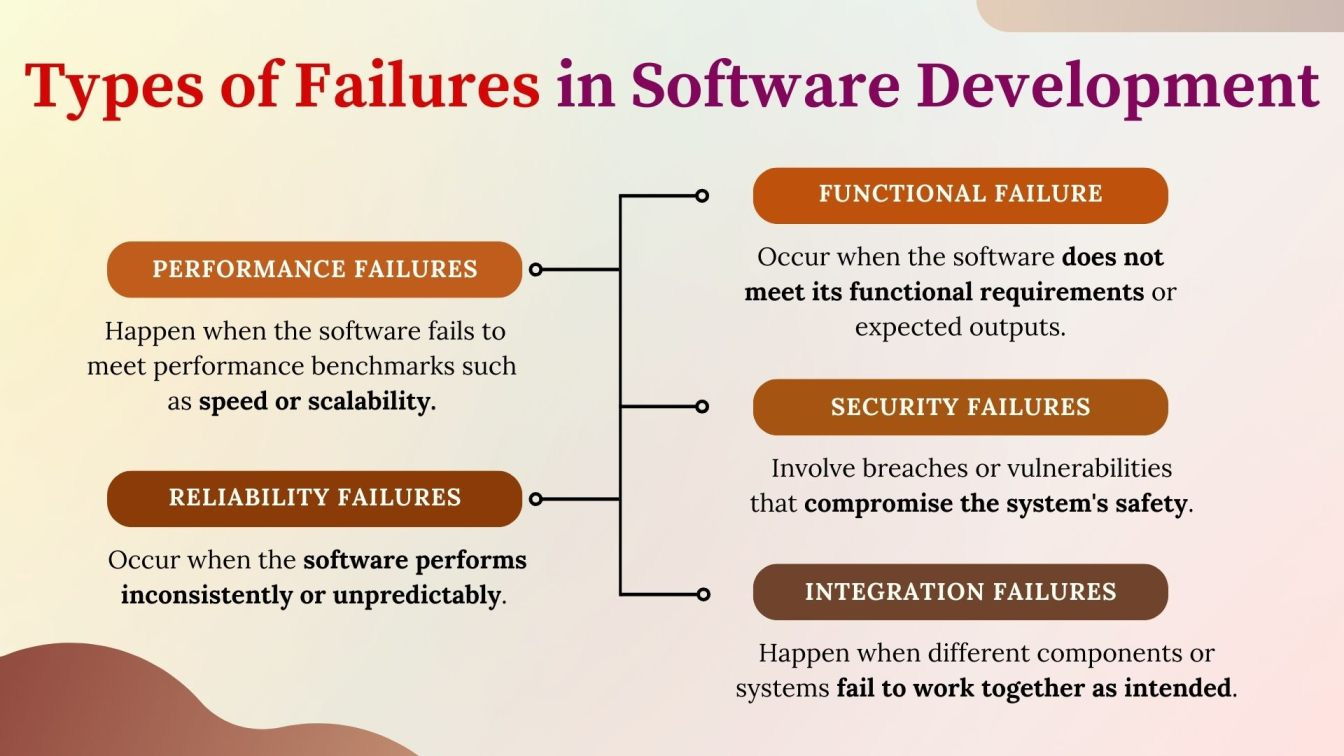
What is a Failure?
A failure occurs when the software stops working or delivers incorrect results. Failures are typically discovered during functional testing or integration/system testing. They can disrupt service and require immediate resolution.
Impact of Failures:
System Disruptions
Decreased User Trust
Urgency in Fixes and Debugging
Loss of Reputation
Key Takeaway: Failures are the most noticeable issue and often require immediate action to prevent business disruptions.
Why Is It Important to Differentiate Between Bug, Defect, Error, Fault, and Failure?
Clear Communication: Helps development and testing teams understand the issue and communicate more effectively.
Efficient Troubleshooting: Identifying the exact type of issue enables quicker root cause analysis.
Effective Use of Automation: Clear distinctions help in utilizing automation tools for early detection.
Prioritization of Fixes: Knowing which issue requires immediate attention (e.g., defects) helps prioritize work.
AI and Automation in Identifying Bugs and Defects
AI-driven testing tools can quickly identify and fix bugs, defects, and other issues. By automating bug tracking and employing predictive analytics, you can ensure faster and more accurate testing.
Top Tools for Bug Detection:
Testim: AI-assisted test creation & maintenance
Mabl: Intelligent test execution and visual UI testing
Applitools: AI-powered visual regression for UI consistency
Key Takeaway: AI tools enhance the speed and accuracy of bug detection, reducing manual effort and enhancing test coverage.
People Also Ask
👉 Are all bugs considered defects? Not all bugs are defects, but all defects result from bugs that affect functionality.
👉 How do you prevent errors from becoming failures? Early detection and resolution through rigorous testing can prevent errors from escalating into failures.
👉 What tools can help identify and track these issues? Tools like JIRA, Selenium, and TestRail can help identify and track bugs, defects, and errors effectively.